前言
针对不同平台/语言下的命令执行是不相同的,存在很大的差异性。因此,这里对不同平台/语言下的命令执行函数进行深入的探究分析。
文章开头会对不同平台(Linux、Windows)下:终端的指令执行、语言(PHP、Java、Python)的命令执行进行介绍分析。后面,主要以PHP语言为对象,针对不同平台,对命令执行函数进行底层深入分析,这个过程包括:PHP内核源码的编译、运行、调试、审计等,其它语言分析原理思路类似。19
该系列分析文章主要分为四部分,如下:
- 第一部分:命令执行底层原理探究-PHP (一)
针对不同平台(Linux、Windows)下:终端的指令执行、语言(PHP、Java、Python)的命令执行进行介绍分析。
- 第二部分:命令执行底层原理探究-PHP (二)
主要以PHP语言为对象,针对不同平台,进行环境准备、PHP内核源码的编译、运行、调试等。
- 第三部分:命令执行底层原理探究-PHP (三)
针对Windows平台下,PHP命令执行函数的底层原理分析。
- 第四部分:命令执行底层原理探究-PHP (四)
针对Linux平台下,PHP命令执行函数的底层原理分析。
本文 《 命令执行底层原理探究-PHP (一) 》 主要讲述的是第一部分:针对不同平台(Linux、Windows)下:终端的指令执行、语言(PHP、Java、Python)的命令执行进行介绍分析。
平台语言
不同平台终端指令执行
不同平台终端中执行的命令方式一般有两种:自身终端封装的指令(内置)、终端下调用其它目录下的可执行程序(外部)。
Linux
Linux下终端一般为 /bin/bash 、 /bin/sh 、 /bin/zsh 等,这里以 bash 终端为例测试。
以Linux为例【Windows等平台原理同Linux类似】,Linux下终端内建(内置)的指令类型为: shell built-in command 。
所谓 shell built-in command ,就是那些内建在 linux shell 里面的 command 指令。
通常情况下,在 linux shell 下面执行一个 command 指令,shell会查找 command 是否为 built-in command 类型,对于 built-in command 指令类型,shell会自己解释执行,而无需fork一个 child process 子进程来执行该 command 指令;对于,不是 built-in command 指令类型,shell会从环境变量中按顺序搜索该 command 指令,如果能查到则会fork一个 child process 子进程来执行该 command 指令;然而,对于找不到的 command 指令,一般为:执行的指令不存在、指令未加入到环境变量中。
那么如何进行终端内建指令的判断与查看呢,对于内建指令可以使用 type 指令去判断
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─# type echo
echo is a shell builtin
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─# type whoami
whoami is /usr/bin/whoami
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─#
或着 也可以使用其它指令进行查找判断: which、where
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─# which echo
echo: shell built-in command
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─# which whoami
/usr/bin/whoami
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─#
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─# where echo
echo: shell built-in command
echo
/bin/echo
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─# where whoami
/usr/bin/whoami
/bin/whoami
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─#
注意:在Linux平台,有些命令虽然为内建命令,但是系统关键目录也存在其可执行文件。
这里也可以使用 enable 或 help 指令,查看终端内建的所有指令
- 第一种: enable 指令
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─# enable
-
.
:
[
alias
autoload
bg
bindkey
break
builtin
bye
cd
chdir
command
compadd
comparguments
compcall
compctl
compdescribe
compfiles
compgroups
compquote
compset
comptags
comptry
compvalues
continue
declare
dirs
disable
disown
echo
echotc
echoti
emulate
enable
eval
exec
exit
export
false
fc
fg
float
functions
getln
getopts
hash
history
integer
jobs
kill
let
limit
local
log
logout
noglob
popd
print
printf
private
pushd
pushln
pwd
r
read
readonly
rehash
return
sched
set
setopt
shift
source
suspend
test
times
trap
true
ttyctl
type
typeset
ulimit
umask
unalias
unfunction
unhash
unlimit
unset
unsetopt
vared
wait
whence
where
which
zcompile
zformat
zle
zmodload
zparseopts
zregexparse
zstat
zstyle
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─#
- 第二种: help 指令
接着对终端(内置|外置)命令进行测试,测试终端 /bin/zsh :
- 测试: whoami 指令
先对 whoami 指令进行类型探测与指令定位查询
# 指令探测:非内置指令
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─# type whoami
whoami is /usr/bin/whoami
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─#
# 指令定位查询:搜索发现系统特殊目录存在`whoami`可执行程序
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─# where whoami
/usr/bin/whoami
/bin/whoami
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─#
注意: /bin 目录为 /usr/bin 目录的链接
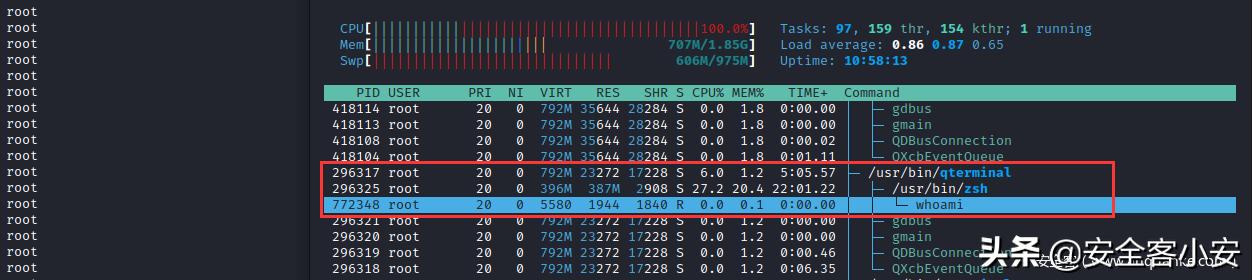
然后,在 zsh 终端写入 For循环 执行 whoami 指令查看是否为内部执行或外部调用
for n in {0..10000000}; do whoami ; done
另一侧,使用 htop 动态进程监控程序对该终端进行监控,可发现 whoami 指令并非 zsh 终端内置封装的指令
- 测试: echo 指令
同样,对 echo 指令进行类型探测与指令定位查询
# 指令探测:内置指令
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─# type echo
echo is a shell builtin
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─#
# 指令定位查询:搜索发现系统特殊目录存在`echo`可执行程序,同时还发现存在`echo: shell built-in command`【终端内置指令】
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─# where echo
echo: shell built-in command
/usr/bin/echo
/bin/echo
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面]
└─#
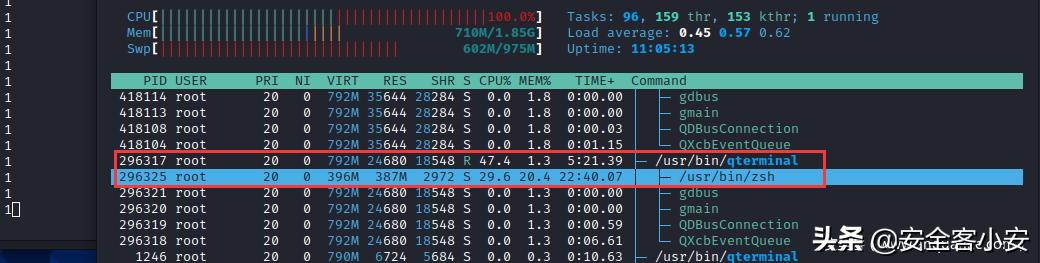
然后,在 zsh 终端写入 For循环 执行 echo 指令查看是否为内部执行或外部调用
for n in {0..10000000}; do echo 1 ; done
另一侧,使用 htop 动态进程监控程序对该终端进行监控,可以发现 echo 指令为 zsh 终端内置封装的指令,并未出现外部调用
Windows
Windows下终端一般为 cmd.exe 、 powershell.exe 等,这里以 cmd 来测试。终端指令执行原理同上述Linux讲解原理相同,分为终端内置指令与外部调用指令。
那么,针对Windows平台可执行终端,如何进行终端内建指令的判断与查看呢。可惜Windows平台终端不像Linux终端存在相应的 type 指令进行判断与 enable 、 help 指令查看所有内建指令。不过在Windows终端里可以借助 where 或 set PATH 指令进行指令判断。
- 第一种: where 指令【不太友好】
从系统环境变量 PATH 里面定位查询(注意人为增添的环境变量的影响),如果能查到一般来说可以判定为外部调用指令(排除非系统特殊目录),否则为内部调用指令(排除不存在指令)
# 外部调用指令
C:\Users\Qftm>where whoami
C:\Windows\System32\whoami.exe
C:\Users\Qftm>
# 内部调用指令
C:\Users\Qftm>where cd
INFO: Could not find files for the given pattern(s).
C:\Users\Qftm>
# 不存在指令
C:\Users\Qftm>where qftm
INFO: Could not find files for the given pattern(s).
C:\Users\Qftm>
# 内部调用指令(排除人为增添的环境变量的影响)(排除非系统特殊目录)
C:\Users\Qftm>where echo
D:\QSoftware\W3Server\phpstudy2019\Extensions\MySQL5.7.26\bin\echo.exe
C:\Users\Qftm>
- 第二种: set path 指令【友好】
将系统环境变量临时设置为 null ,然后对指令进行帮助查询,如果能查到则判定为内置指令,否则为外部调用。
# path置空
C:\Users\Qftm>set path=
C:\Users\Qftm>path
PATH=(null)
C:\Users\Qftm>
# 内部调用指令
C:\Users\Qftm>cd /?
Displays the name of or changes the current directory.
CHDIR [/D] [drive:][path]
CHDIR [..]
CD [/D] [drive:][path]
CD [..]
.. Specifies that you want to change to the parent directory.
Type CD drive: to display the current directory in the specified drive.
Type CD without parameters to display the current drive and directory.
Use the /D switch to change current drive in addition to changing current
directory for a drive.
If Command Extensions are enabled CHDIR changes as follows:
The current directory string is converted to use the same case as
the on disk names. So CD C:\TEMP would actually set the current
directory to C:\Temp if that is the case on disk.
CHDIR command does not treat spaces as delimiters, so it is possible to
CD into a subdirectory name that contains a space without surrounding
the name with quotes. For example:
cd \winnt\profiles\username\programs\start menu
is the same as:
cd "\winnt\profiles\username\programs\start menu"
which is what you would have to type if extensions were disabled.
C:\Users\Qftm>
# 外部调用指令
C:\Users\Qftm>whoami /?
'whoami' is not recognized as an internal or external command,
operable program or batch file.
C:\Users\Qftm>
# 不存在指令
C:\Users\Qftm>qftm /?
'qftm' is not recognized as an internal or external command,
operable program or batch file.
C:\Users\Qftm>
注意:Windows下终端 help 指令并不能够查询终端内建指令:首先 help 指令为外部调用指令,然后 help 指令查询出的所有指令=(内建指令+外部指令)
# help:属于外部指令
C:\Users\Qftm>where help
C:\Windows\System32\help.exe
C:\Users\Qftm>
# help:内建指令+外部指令(不同于Linux下bash等终端)
C:\Users\Qftm>help
For more information on a specific command, type HELP command-name
ASSOC Displays or modifies file extension associations.
ATTRIB Displays or changes file attributes.
BREAK Sets or clears extended CTRL+C checking.
BCDEDIT Sets properties in boot database to control boot loading.
CACLS Displays or modifies access control lists (ACLs) of files.
CALL Calls one batch program from another.
CD Displays the name of or changes the current directory.
CHCP Displays or sets the active code page number.
CHDIR Displays the name of or changes the current directory.
CHKDSK Checks a disk and displays a status report.
CHKNTFS Displays or modifies the checking of disk at boot time.
CLS Clears the screen.
CMD Starts a new instance of the Windows command interpreter.
COLOR Sets the default console foreground and background colors.
COMP Compares the contents of two files or sets of files.
COMPACT Displays or alters the compression of files on NTFS partitions.
CONVERT Converts FAT volumes to NTFS. You cannot convert the
current drive.
COPY Copies one or more files to another location.
DATE Displays or sets the date.
DEL Deletes one or more files.
DIR Displays a list of files and subdirectories in a directory.
DISKPART Displays or configures Disk Partition properties.
DOSKEY Edits command lines, recalls Windows commands, and
creates macros.
DRIVERQUERY Displays current device driver status and properties.
ECHO Displays messages, or turns command echoing on or off.
ENDLOCAL Ends localization of environment changes in a batch file.
ERASE Deletes one or more files.
EXIT Quits the CMD.EXE program (command interpreter).
FC Compares two files or sets of files, and displays the
differences between them.
FIND Searches for a text string in a file or files.
FINDSTR Searches for strings in files.
FOR Runs a specified command for each file in a set of files.
FORMAT Formats a disk for use with Windows.
FSUTIL Displays or configures the file system properties.
FTYPE Displays or modifies file types used in file extension
associations.
GOTO Directs the Windows command interpreter to a labeled line in
a batch program.
GPRESULT Displays Group Policy information for machine or user.
GRAFTABL Enables Windows to display an extended character set in
graphics mode.
HELP Provides Help information for Windows commands.
ICACLS Display, modify, backup, or restore ACLs for files and
directories.
IF Performs conditional processing in batch programs.
LABEL Creates, changes, or deletes the volume label of a disk.
MD Creates a directory.
MKDIR Creates a directory.
MKLINK Creates Symbolic Links and Hard Links
MODE Configures a system device.
MORE Displays output one screen at a time.
MOVE Moves one or more files from one directory to another
directory.
OPENFILES Displays files opened by remote users for a file share.
PATH Displays or sets a search path for executable files.
PAUSE Suspends processing of a batch file and displays a message.
POPD Restores the previous value of the current directory saved by
PUSHD.
PRINT Prints a text file.
PROMPT Changes the Windows command prompt.
PUSHD Saves the current directory then changes it.
RD Removes a directory.
RECOVER Recovers readable information from a bad or defective disk.
REM Records comments (remarks) in batch files or CONFIG.SYS.
REN Renames a file or files.
RENAME Renames a file or files.
REPLACE Replaces files.
RMDIR Removes a directory.
ROBOCOPY Advanced utility to copy files and directory trees
SET Displays, sets, or removes Windows environment variables.
SETLOCAL Begins localization of environment changes in a batch file.
SC Displays or configures services (background processes).
SCHTASKS Schedules commands and programs to run on a computer.
SHIFT Shifts the position of replaceable parameters in batch files.
SHUTDOWN Allows proper local or remote shutdown of machine.
SORT Sorts input.
START Starts a separate window to run a specified program or command.
SUBST Associates a path with a drive letter.
SYSTEMINFO Displays machine specific properties and configuration.
TASKLIST Displays all currently running tasks including services.
TASKKILL Kill or stop a running process or application.
TIME Displays or sets the system time.
TITLE Sets the window title for a CMD.EXE session.
TREE Graphically displays the directory structure of a drive or
path.
TYPE Displays the contents of a text file.
VER Displays the Windows version.
VERIFY Tells Windows whether to verify that your files are written
correctly to a disk.
VOL Displays a disk volume label and serial number.
XCOPY Copies files and directory trees.
WMIC Displays WMI information inside interactive command shell.
For more information on tools see the command-line reference in the online help.
C:\Users\Qftm>
接着对终端(内置|外置)命令进行测试,测试终端 cmd.exe :
- 测试: whoami 指令
先对 whoami 指令进行类型探测与指令定位查询
# 类型探测:外部调用指令
# 定位查询:系统可执行程序
C:\Users\Qftm>where whoami
C:\Windows\System32\whoami.exe
C:\Users\Qftm>
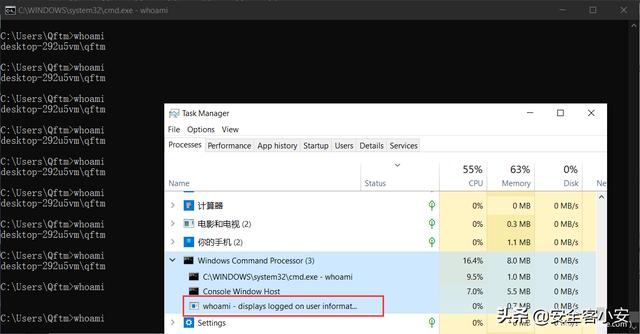
然后,在 cmd 终端写入 For 循环执行 whoami 指令查看是否为内部执行或外部调用
C:\Users\Qftm>for /l %i in (1,1,1000000) do whoami
另一侧,打开任务管理进行 cmd 终端的监控,可发现 whoami 指令并非 cmd.exe 终端内置封装的指令
- 测试: echo 指令
同样,对 echo 指令进行类型探测与指令定位查询
# 类型探测:内部调用指令
# 定位查询:非系统可执行程序
C:\Users\Qftm>where echo
D:\QSoftware\W3Server\phpstudy2019\Extensions\MySQL5.7.26\bin\echo.exe
C:\Users\Qftm>
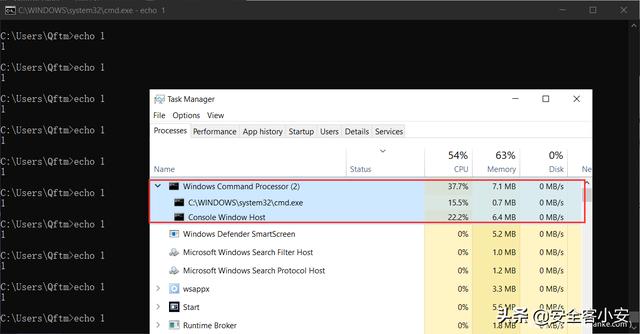
然后,在 cmd 终端写入 For 循环执行 echo 指令查看是否为内部执行或外部调用
for /l %i in (1,1,1000000) do echo 1
另一侧,打开任务管理进行 cmd 终端的监控,可以发现 echo 指令为终端内置封装的指令,并未出现外部调用
语言差异
针对命令执行函数,底层实现上是否存在命令执行程序 cmd.exe 、 /bin/sh 、 /bin/bash 等,去执行命令执行函数传入的参数【系统命令】。这个过程相当于底层是否引入第三方可执行终端去执行相应命令。
比如: 可执行函数(系统命令)
CommandExecFunc(echo 111 > shell.txt); //echo是一个可执行程序
上述命令执行函数模型在【Linux平台/windows平台】不同语言下面执行效果不同。
PHP
PHP - 底层调用系统终端,执行命令 Mode => Window:cmd.exe /c Command || Linux:sh -c Command
在 PHP 语言里面,针对Linux平台,系统命令 echo 111 > shell.txt 传入 CommandExecFunc 函数,最终在底层相当于执行 /bin/sh -c echo 111 > shell.txt 。成功创建文件 shell.txt 【执行过程相当于:在 /bin/sh 终端下执行命令 echo 111 ,并将echo结果通过重定向符写入文件 shell.txt 中。这里的重定向符不是echo中的参数或字符串,而是在 /bin/sh 下面起特殊作用。这里的echo并不是可执行程序 /bin/echo ,而是 /bin/sh 执行终端中的内建命令】【进程相关:一个进程 /bin/sh ,在 /bin/sh 进程中执行系统命令,而不是执行系统程序】
- 跟踪一下程序执行流程: For Linux
利用 strace 程序执行监视可知,底层通过 execve 系统调用来启动相关进程、然后通过 /bin/sh 进程来执行相关指令(此处 echo 为 sh 内置指令)。
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面/CodeDebug/php]
└─# strace -f -e execve php -r "system('echo 111 > shell.txt');"
execve("/usr/bin/php", ["php", "-r", "system('echo 111 > shell.txt');"], 0x7ffd51277198 /* 53 vars */) = 0
strace: Process 3436 attached
[pid 3436] execve("/bin/sh", ["sh", "-c", "echo 111 > shell.txt"], 0x562c96ef1eb0 /* 53 vars */) = 0
[pid 3436] +++ exited with 0 +++
--- SIGCHLD {si_signo=SIGCHLD, si_code=CLD_EXITED, si_pid=3436, si_uid=0, si_status=0, si_utime=0, si_stime=0} ---
+++ exited with 0 +++
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面/CodeDebug/php]
└─# ls
shell.txt
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面/CodeDebug/php]
└─#
同理,针对Windows平台:系统命令 echo 111 > shell.txt 传入 CommandExecFunc 函数,最终在底层相当于执行 cmd.exe /c echo 111 > shell.txt 。成功创建文件 shell.txt 【执行过程相当于:在 cmd 终端下执行命令 echo 111 ,并将echo结果通过重定向符写入文件 shell.txt 中。【进程相关:一个进程 cmd.exe ,在 cmd.exe 进程中执行系统命令,而不是执行系统程序】
- 跟踪一下程序执行流程: For Windows
使用OD动态调试,加载 php.exe 程序,对相关创建进程的系统API下断点(如果不知道是那个 CreateProcess API 可以把查询到的都进行断点即可)
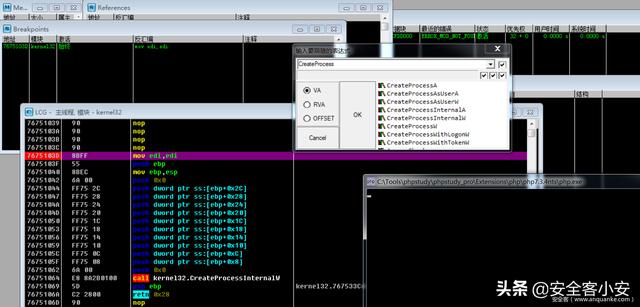
断点之后,F9使程序运行至用户交互处,然后输入PHP执行指令 system(‘echo 111 > shell.txt’);
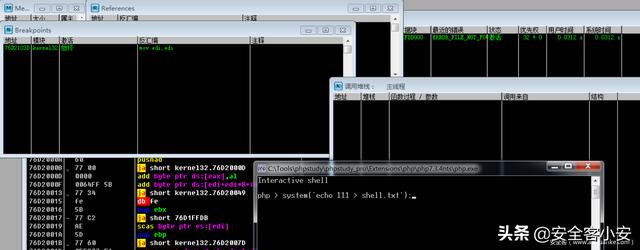
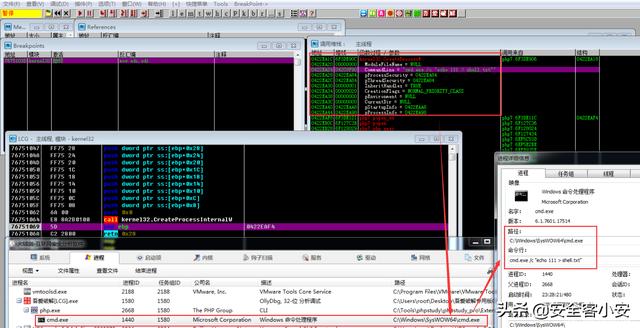
运行PHP执行指令后,程序可到断点处,然后通过调用栈可知:底层通过 CreateProcessW 系统API调用来启动相关进程、然后通过 cmd 进程来执行相关指令(此处 echo 为 cmd 内置指令)(注意:这里也可查看到PHP程序的完整调用链)
Java
Java - 底层不调用系统终端,自己启动传入的可执行程序 Mode => Window:Command || Linux:Command
但是在 Java 语言里面,针对Linux平台,系统命令 echo 111 > shell.txt 传入 CommandExecFunc 函数,最终在底层相当于执行 /bin/echo 111 > shell.txt 成功打印一个字符串 “111 > shell.txt” 并没有创建文件 shell.txt 。【执行过程相当于:运行可执行程序 /bin/echo 并传入参数 111 > shell.txt 进行打印输出,这里的特殊字符 > 被当作普通字符串被echo程序打印。这里的 echo 作为可执行程序出现,而不是终端中的命令】【进程相关:一个进程 /bin/echo ,在 /bin/echo 进程中传入字符串参数 111 > shell.txt 进行打印输出】【有关可执行程序怎么查询:从环境变量中进行查询】
测试代码如下
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
import java.lang.Runtime;
public class CommandExec1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
String str = IOUtils.toString(Runtime.getRuntime().exec("whoami").getInputStream());
System.out.println(str);
}
catch(Exception a){
System.out.println(a);
}
}
}
- 跟踪一下程序执行流程: For Linux
程序执行监视情况:从系统环境变量中查找输入的指令可执行程序位置,然后由 execve 系统调用来启动相关程序进程(并未涉及系统终端调用)。
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面/CodeDebug/java]
└─# strace -f -e execve java CommandExec1
execve("/usr/bin/java", ["java", "CommandExec1"], 0x7ffdb259ee90 /* 53 vars */) = 0
strace: Process 3923 attached
Picked up _JAVA_OPTIONS: -Dawt.useSystemAAFontSettings=on -Dswing.aatext=true
[pid 3923] --- SIGSEGV {si_signo=SIGSEGV, si_code=SEGV_MAPERR, si_addr=NULL} ---
strace: Process 3924 attached
strace: Process 3925 attached
strace: Process 3926 attached
strace: Process 3927 attached
strace: Process 3928 attached
strace: Process 3929 attached
strace: Process 3930 attached
strace: Process 3931 attached
strace: Process 3932 attached
[pid 3932] execve("/mnt/hgfs/QSec/Pentest/Red-Team/\347\245\236\345\205\265\345\210\251\345\231\250/Windows/VSCode/VSCode-linux-x64/whoami", ["whoami"], 0x7ffd28368b80 /* 53 vars */) = -1 ENOENT (没有那个文件或目录)
[pid 3932] execve("/usr/local/sbin/whoami", ["whoami"], 0x7ffd28368b80 /* 53 vars */) = -1 ENOENT (没有那个文件或目录)
[pid 3932] execve("/usr/local/bin/whoami", ["whoami"], 0x7ffd28368b80 /* 53 vars */) = -1 ENOENT (没有那个文件或目录)
[pid 3932] execve("/usr/sbin/whoami", ["whoami"], 0x7ffd28368b80 /* 53 vars */) = -1 ENOENT (没有那个文件或目录)
[pid 3932] execve("/usr/bin/whoami", ["whoami"], 0x7ffd28368b80 /* 53 vars */) = 0
[pid 3932] +++ exited with 0 +++
[pid 3923] --- SIGCHLD {si_signo=SIGCHLD, si_code=CLD_EXITED, si_pid=3932, si_uid=0, si_status=0, si_utime=0, si_stime=0} ---
strace: Process 3933 attached
root
[pid 3931] +++ exited with 0 +++
[pid 3927] +++ exited with 0 +++
[pid 3924] +++ exited with 0 +++
[pid 3923] +++ exited with 0 +++
[pid 3933] +++ exited with 0 +++
[pid 3930] +++ exited with 0 +++
[pid 3929] +++ exited with 0 +++
[pid 3928] +++ exited with 0 +++
[pid 3926] +++ exited with 0 +++
[pid 3925] +++ exited with 0 +++
+++ exited with 0 +++
┌──(roottoor)-[~/桌面/CodeDebug/java]
└─#
同理,针对Windows平台,系统命令 echo 111 > shell.txt 传入 CommandExecFunc 函数,最终在底层相当于执行 系统环境变量/echo.exe 111 > shell.txt 成功打印一个字符串 “111 > shell.txt” 并没有创建文件 shell.txt 。
但是,正常情况下,这里执行上述指令会报错,因为Windows平台,默认情况下系统环境变量中不存在 echo.exe 可执行程序,导致指令无法正常执行
# 无法定位echo可执行程序
D:\QSec\Code-Audit\Tools\Java\Kits\RCE>where echo
INFO: Could not find files for the given pattern(s).
D:\QSec\Code-Audit\Tools\Java\Kits\RCE>where whoami
C:\Windows\System32\whoami.exe
D:\QSec\Code-Audit\Tools\Java\Kits\RCE>
# 执行报错
D:\QSec\Code-Audit\Tools\Java\Kits\RCE>javac RuntimeRCE.java
D:\QSec\Code-Audit\Tools\Java\Kits\RCE>java RuntimeRCE
java.io.IOException: Cannot run program "echo": CreateProcess error=2, The system cannot find the file specified
D:\QSec\Code-Audit\Tools\Java\Kits\RCE>
Python
Python - 底层调用系统终端,执行命令 Mode => Window:cmd.exe /c Command || Linux:sh -c Command
而 Python 语言,命令执行函数底层原理实现同 PHP 语言。
总结起来,也就是,命令执行函数执行分为两类,一类:传入的命令仅仅作为可执行终端中的命令执行;另一类:传入的命令仅仅是运行传入的命令中的可执行程序。对象不同,一类:是底层语言系统终端帮我们执行传入的命令;另一类:是自己启动传入的可执行程序。
参考链接
- Build your own PHP on Windows
- Visual Studio docs
- Visual Studio Code docs
- 《PHP 7底层设计与源码实现+PHP7内核剖析》
- 深入理解 PHP 内核
- WINDOWS下用VSCODE调试PHP7源代码
- 调式PHP源码
- 用vscode调试php源码
- GDB: The GNU Project Debugger
- CreateProcessW function
- 命令注入成因小谈
- 浅谈从PHP内核层面防范PHP WebShell
- Program execution Functions
- linux系统调用
- system calls