Springboot整合ip2region实现用户ip归属地获取
1、 ip2region 是什么
ip2region - 是一个离线ip地址定位库和ip定位数据管理框架,10微秒级别的查询效率,提供了众多主流编程语言的 xdb 数据生成和查询客户端实现。
2、ip2region 特性
2.1、ip 数据管理框架
xdb 支持亿级别的 ip 数据段行数,默认的 region 信息都固定了格式:国家|区域|省份|城市|isp,缺省的地域信息默认是0。 region 信息支持完全自定义,例如:你
可以在 region 中追加特定业务需求的数据,例如:gps信息/国际统一地域信息编码/邮编等。也就是你完全可以使用 ip2region 来管理你自己的 ip 定位数据。
2.2、数据去重和压缩
xdb 格式生成程序会自动去重和压缩部分数据,默认的全部 ip 数据,生成的 ip2region.xdb 数据库是 11mib,随着数据的详细度增加数据库的大小也慢慢增大。
2.3、极速查询响应
即使是完全基于 xdb 文件的查询,单次查询响应时间在十微秒级别,可通过如下两种方式开启内存加速查询:
- vindex 索引缓存 :使用固定的 512kib 的内存空间缓存 vector index 数据,减少一次 io 磁盘操作,保持平均查询效率稳定在10-20微秒之间。
- xdb 整个文件缓存:将整个 xdb 文件全部加载到内存,内存占用等同于 xdb 文件大小,无磁盘 io 操作,保持微秒级别的查询效率。
3、ip2region的使用
步骤:
1、生成ip2region.xdb文件,做好ip2region的相关配置
2、从请求中获取用户的ip地址
3、通过ip2redion.xdb中的对应关系找到用户的ip对应的地点(格式:`国家|区域|省份|城市|运营商`,缺省的地域信息默认是0)
3.1、生成ip2region.xdb文件
下载ip2region的master分支
编译安装
通过 maven 来编译可运行 jar 程序:
# cd 到 maker/java 根目录 mvn clean compile package
然会会在当前目录的 target 目录下得到一个 ip2region-maker-{version}.jar 的打包文件。
数据生成
通过 java -jar ip2region-maker-{version}.jar 来生成 ip2region.xdb 二进制文件:
➜ java git:(java_xdb_maker) ✗ java -jar ./target/ip2region-maker-1.0.0.jar
ip2region xdb maker
java -jar ip2region-maker-{version}.jar [command options]
options:
--src string source ip text file path
--dst string destination binary xdb file path
例如,通过默认的 data/ip.merge.txt 原数据,在当前目录生成一个 ip2region.xdb 二进制文件:
在控制台中输入:java -jar ./target/ip2region-maker-1.0.0.jar --src=../../data/ip.merge.txt --dst=./ip2region.xdb
3.2、导入ip2region的依赖
org.lionsoul
ip2region
2.6.3
3.3、从请求中获取用户的ip
1.全局获取httpservletrequest的工具类
/**
* 全局获取httpservletrequest、httpservletresponse的工具类
*/
public class httpcontextutil {
private httpcontextutil() {
}
public static httpservletrequest gethttpservletrequest() {
return ((servletrequestattributes) objects.requirenonnull(requestcontextholder.getrequestattributes())).getrequest();
}
public static httpservletresponse gethttpservletresponse() {
return ((servletrequestattributes) objects.requirenonnull(requestcontextholder.getrequestattributes())).getresponse();
}
}
2.从请求中获取ip的类
public class iputil {
private static final string unknown = "unknown";
protected iputil() {
}
/**
* 获取 ip地址
* 使用 nginx等反向代理软件, 则不能通过 request.getremoteaddr()获取 ip地址
* 如果使用了多级反向代理的话,x-forwarded-for的值并不止一个,而是一串ip地址,
* x-forwarded-for中第一个非 unknown的有效ip字符串,则为真实ip地址
*/
public static string getipaddr(httpservletrequest request) {
string ip = request.getheader("x-forwarded-for");
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || unknown.equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = request.getheader("proxy-client-ip");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || unknown.equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = request.getheader("wl-proxy-client-ip");
}
if (ip == null || ip.length() == 0 || unknown.equalsignorecase(ip)) {
ip = request.getremoteaddr();
}
return "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1".equals(ip) ? "127.0.0.1" : ip;
}
}
3.通过ip从ip2region.xdb中获取用户归属地
共有三种方法:
- 完全基于文件查询
- 缓存vectorindex索引
- 缓存整个xdb文件
public class addressutil {
public static string dbpath = "src/main/resources/ip2region/ip2region.xdb";
public static string region = "unkown";
//方法一:完全基于文件的查询
public static string getinfobyfie(string ip) throws ioexception {
// 1、创建 searcher 对象
searcher searcher = null;
try {
searcher = searcher.newwithfileonly(dbpath);
} catch (ioexception e) {
system.out.printf("failed to create searcher with `%s`: %s\n", dbpath, e);
return "";
}
// 2、查询
try {
//ip = "119.39.183.117";
long stime = system.nanotime();
region = searcher.searchbystr(ip);
long cost = timeunit.nanoseconds.tomicros((long) (system.nanotime() - stime));
system.out.printf("{region: %s, iocount: %d, took: %d μs}\n", region, searcher.getiocount(), cost);
} catch (exception e) {
system.out.printf("failed to search(%s): %s\n", ip, e);
}
return region;
// 备注:并发使用,每个线程需要创建一个独立的 searcher 对象单独使用。
}
//方法二:缓存 vectorindex 索引
//我们可以提前从 xdb 文件中加载出来 vectorindex 数据,然后全局缓存,
// 每次创建 searcher 对象的时候使用全局的 vectorindex 缓存可以减少一次固定的 io 操作,从而加速查询,减少 io 压力。
public static string getinfobyvectorindex(string ip) throws ioexception {
// 1、从 dbpath 中预先加载 vectorindex 缓存,并且把这个得到的数据作为全局变量,后续反复使用。
byte[] vindex;
try {
vindex = searcher.loadvectorindexfromfile(dbpath);
} catch (exception e) {
system.out.printf("failed to load vector index from `%s`: %s\n", dbpath, e);
return "";
}
// 2、使用全局的 vindex 创建带 vectorindex 缓存的查询对象。
searcher searcher;
try {
searcher = searcher.newwithvectorindex(dbpath, vindex);
} catch (exception e) {
system.out.printf("failed to create vectorindex cached searcher with `%s`: %s\n", dbpath, e);
return "";
}
// 2、查询
try {
//ip = "119.39.183.117";
long stime = system.nanotime();
region = searcher.searchbystr(ip);
long cost = timeunit.nanoseconds.tomicros((long) (system.nanotime() - stime));
system.out.printf("{region: %s, iocount: %d, took: %d μs}\n", region, searcher.getiocount(), cost);
} catch (exception e) {
system.out.printf("failed to search(%s): %s\n", ip, e);
}
return region;
// 备注:每个线程需要单独创建一个独立的 searcher 对象,但是都共享全局的制度 vindex 缓存。
}
//方法三:缓存整个 xdb 数据
//我们也可以预先加载整个 ip2region.xdb 的数据到内存,
//然后基于这个数据创建查询对象来实现完全基于文件的查询,类似之前的 memory search。
public static string getinfobybuffer(string ip) throws ioexception {
// 1、从 dbpath 中预先加载 vectorindex 缓存,并且把这个得到的数据作为全局变量,后续反复使用。
byte[] vindex;
try {
vindex = searcher.loadvectorindexfromfile(dbpath);
} catch (exception e) {
system.out.printf("failed to load vector index from `%s`: %s\n", dbpath, e);
return "";
}
// 2、使用全局的 vindex 创建带 vectorindex 缓存的查询对象。
searcher searcher;
try {
searcher = searcher.newwithvectorindex(dbpath, vindex);
} catch (exception e) {
system.out.printf("failed to create vectorindex cached searcher with `%s`: %s\n", dbpath, e);
return "";
}
// 2、查询
try {
//ip = "119.39.183.117";
long stime = system.nanotime();
string region = searcher.searchbystr(ip);
long cost = timeunit.nanoseconds.tomicros((long) (system.nanotime() - stime));
system.out.printf("{region: %s, iocount: %d, took: %d μs}\n", region, searcher.getiocount(), cost);
} catch (exception e) {
system.out.printf("failed to search(%s): %s\n", ip, e);
}
return region;
// 备注:每个线程需要单独创建一个独立的 searcher 对象,但是都共享全局的制度 vindex 缓存。
}
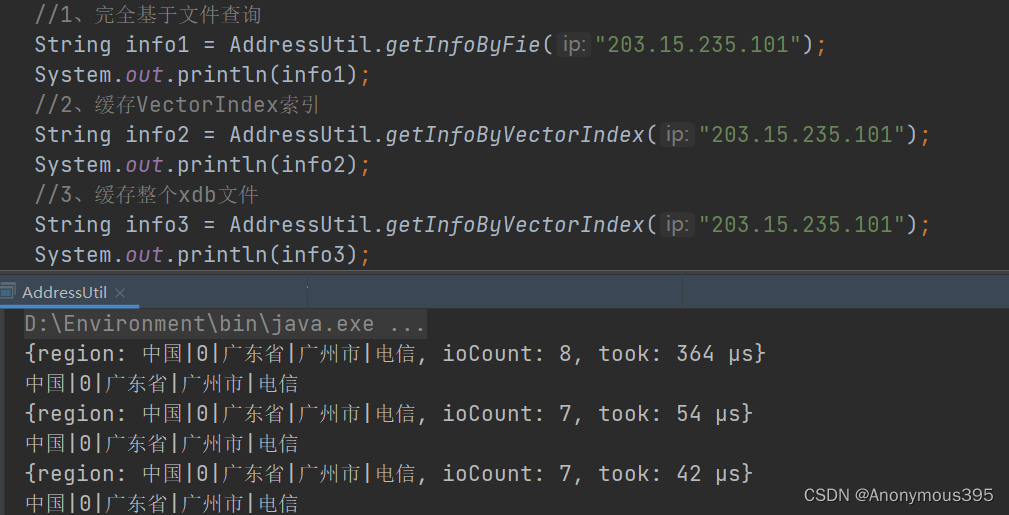
public static void main(string[] args) throws ioexception {
//1、完全基于文件查询
string info1 = addressutil.getinfobyfie("203.15.235.101");
system.out.println(info1);
//2、缓存vectorindex索引
string info2 = addressutil.getinfobyvectorindex("203.15.235.101");
system.out.println(info2);
//3、缓存整个xdb文件
string info3 = addressutil.getinfobyvectorindex("203.15.235.101");
system.out.println(info3);
}
}
4.测试结果
到此这篇关于springboot整合ip2region实现用户ip归属地获取的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关springboot ip2region获取ip归属地内容请搜索代码网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持代码网!
推荐阅读
-

IDEA中使用Gradle构建项目中文报GBK错误的解决方案
-

将Java应用做成exe可执行软件的流程步骤
-
SpringBoot实现多种来源的Zip多层目录打包下载
需要将一批文件(可能分布在不同目录、不同来源)打包成zip格式,按目录结构导出给用户下载。1.核心思路支持将本地服务器上的文...
-
Java中减少if-else的设计模式和优化技巧
前言“过于依赖if-else不仅会让代码变得臃肿不堪,还会使维护成本大大增加。其实,if-else虽然是最基础的条件分支,...
-

Spring Boot 中使用 Drools 规则引擎的完整步骤
-
Spring Boot整合Drools规则引擎实战指南及最佳实践
一、drools简介与核心概念1.1什么是drools?drools是redhat旗下的开源业务规则管理系统(brms),...
-
Springboot项目瘦身之如何将jar包与lib依赖分开打包
将jar包与lib依赖分开打包方法一:项目和依赖完全分离maven-jar-plugin负责生成jar文件(jar文件中...
-
Spring动态修改bean属性配置key的几种方法
静态配置的局限性先来看一个典型场景。假设我们有一个数据源配置类:@configuration@configurationpr...
-

Java如何判断一个IP是否在给定的网段内
-
从零开始学java之二叉树和哈希表实现代码